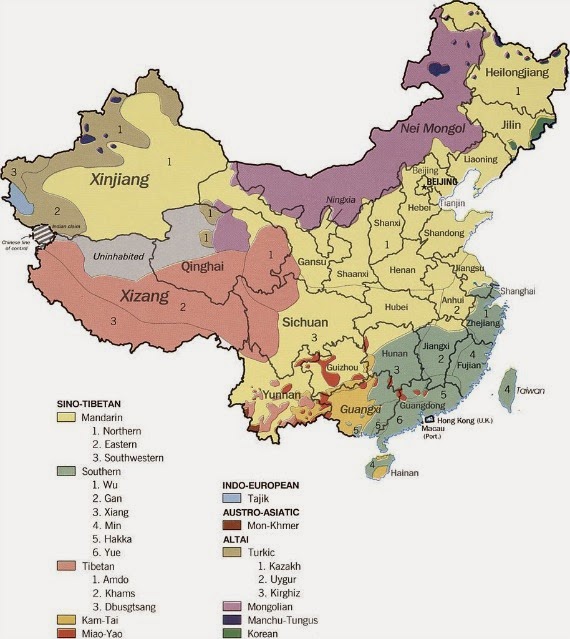
- 汉语 han4 yu3 (literally "the language of Han people"), Chinese language includes many dialects, like shanghainese (上海话 shang4 hai3 hua4), cantonese 广东话 (guang3 dong1 hua4) /粤语 (yue4 yu3), etc.


- 普通话 pu3 tong1 hua4 (literally "Common speech"), Standard Chinese is a standardized form of spoken Chinese based on the Beijing dialect of Mandarin. It is the sole official language of China.
- = 国语 guo2 yu3, (literally "national language"), this term is used in Taiwan, which refers to the standard variety of Chinese.
- = 华语 hua2 yu3, (literally "Chinese language"), it is used in Singapore and Malaysia,
referring to Mandarin Chinese. - so: 普通话 = 国语 = 华语 = Standard Chinese = Mandarin Chinese
- 方言 fang1 yan2 (literally "regional speech"), Dialects , like shanghainese , cantonese, are varieties of Chinese language. "Mountainous South China exhibits more linguistic diversity than the North China Plain. "[1] For example, people from neighbouring villages in Fujian (福建,fu2 jian4) may not understand each other, because their speeches may be mutually unintelligible.
- 少数民族语言 shao3 shu4 min2 zu2 yu3 yan2 (Ethnic minority languages), Minority languages in China are the languages spoken by Chinese ethnic minorities.
reference:
[2]. Photo courtesy: http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/8136043.stm


No comments:
Post a Comment